Which solution prevents microloops from be formed during network convergence time?
A. RSVP-TE
B. LFA
C. Prefix suppression
D. RLFA
Refer to the exhibit.
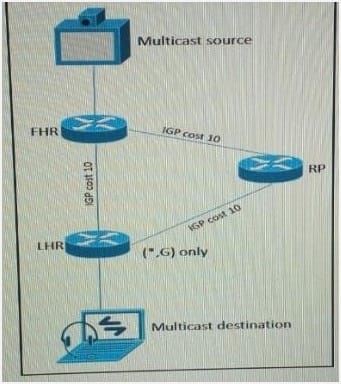
As part of a redesign project, you must predict multicast behavior. What is the resultant multicast traffic receiving on the shared tree( , G), if it is received on the LHR interface indicated?
A. It is dropped due to an unsuccessful RPF check against the multicast receiver
B. It is switched due to a successful RPF check against the routing table
C. It is switched given that no RPF check is performed
D. It is dropped due to an unsuccessful RPF check against the multicast source
As part of network design, two geographically separated data centers must be interconnected using Ethernet-over-MPLS pseudowire. The link between the sites is stable, the topology has no apparent loops, and the root bridges for the respective VLANs are stable and unchanging. Which aspect must be the part of the design to mitigate the risk of connectivity issues between the data centers?
A. Enable Spanning Tree on one data center, and Rapid Reconfiguration of Spanning tree on the other
B. Ensure that the spanning tree diameter for one or more VLANs is not too large.
C. Enable UDLD on the link between the data centers.
D. Enable root guard on the link between the data centers.
A data center provider has designed a network using these requirements
Two data center sites are connected to the public internet
Both data centers are connected to different Internet providers
Both data centers are also directly connected with a private connection for the internal traffic can also be at this direct connection The data center provider has only /19 public IP address block
Under normal conditions, Internet traffic should be routed directly to the data center where the services are located.
When one Internet connections fails to complete traffic for both data centers should be routed by using the remaining Internet connection in which two ways can this routing be achieved? (Choose two)
A. One /20 block is used for the first data center and the second /20 block is used for the second data center. The /20 block from the local data center is sent out without path prepending and the /20 block from the remote data center is sent out with path prepending at both sites
B. One /20 block is used for the first data center and the second /20 block is used for the second data center. Each /20 block is only sent out locally. The /19 block is sent out at both Internet connections for the backup case to reroute the traffic through the remaining internet connection
C. One /20 block is used for the first data center and the second /20 block is used for the second data center. The /20 block from the local data center is sent out with a low BGP local preference and the /20 block from the remote data center is sent out with a higher BGP local preference of both sites
D. BGP will always load-balance the traffic to both data center sites
E. One /20 block is used for the first data center and the second /20 block is used for the second data center. The /20 block from the local data center is sent out with a low BGP weight and the /20 block from the remote data center is sent out with a higher BGP weight at both sites
F. The data center provider must have an additional public IP address block for this routing
What is a correct design consideration of IPv6 MLD snooping?
A. MLD snooping conserves bandwidth on switches.
B. MLD snooping is used to filter all MLD queries.
C. MLD snooping requires IGMP snooping to be implemented.
D. MLD snooping conserves CPU by sharing IPv4 and IPv6 multicast topology.
Which two options are reasons for designing a large OSPF network with multiple areas connected to the backbone? (Choose two)
A. Reduce the number of routes within an area
B. Route tagging capability
C. Simplify logical topology
D. Enhance failure detection
E. Reduce SPF algorithm runs
Refer to the exhibit.
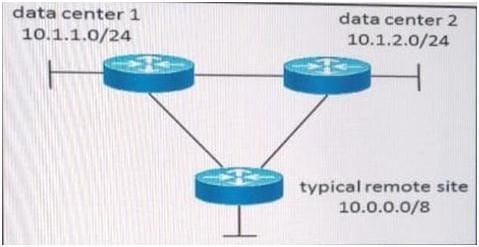
A customer currently has a large EIGRP-based network with several remote sites attached. All remote sites connect to the two corporate data centers, depicted as 10.1.1.0 and 10.1.2.0. The customer has experienced several network-wide failures where neighbors were stuck-in-active and had other network stability issues due to some links flapping. Which two redesign options increase stability and reduce the load on the remote site routers, still maintaining optimal routing between remote sites and the two data centers? (Choose two)
A. Set the data center routers as stub-routers
B. Perform summarization at the data centers, selectively leaking routes sent to the remote sites
C. Perform summarization at the remote sites, selectively leaking routes sent to the data centers
D. Set the hello interval timer to be larger than the hold interval
E. Increase the hold interval to accommodate lost hello packets on error-prone links
Which mechanism should be added to a network design to identify unidirectional Spanning Tree Protocol failures through BPDU loss?
A. Root guard
B. BPDU guard
C. Loop guard
D. UDLD
Which option describes the fundamental design differences between an IP-based network design and a SAN-based?
A. An IP-based design has redundant connectivity in the fabric and high amounts of east- west traffic, whereas a SAN-based design uses redundancy from a dual-attached host, which uses separate fabrics and has very little east-west traffic
B. An IP-based design has redundancy from the host and high amounts of east-west traffic, whereas a SAN-based design uses redundancy in the fabric and very little east-west traffic
C. An IP-based design has redundant connectivity in the fabric and high amounts of east- west traffic, whereas a SAN-based design uses zoning based redundancy which uses separate fabrics and has very little east-west traffic
D. An IP-based design has redundant connectivity in the fabric and very little east-west traffic, whereas a SAN-based design uses redundancy in the host, which uses separate fabrics and has high amounts of east-west traffic
Which multicast technology provides a large, many-to-many connectivity for a new application while minimizing load on the existing network infrastructure?
A. PIM Sparse Mode
B. Bidirectional PIM
C. Any-Source Multicast
D. Source Specific Multicast